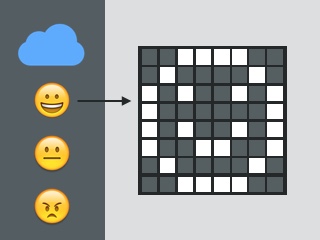
This sample shows how to use Amazon's Alexa Voice Service v1 API to build a simple KinomaJS Alexa client. The application captures and uploads spoken voice in real-time using the PINS library and HTTP chunked transfer encoding. A KinomaJS Canvas object animation provides interactive input voice level and Alexa answer feedback. An Amazon developer account and Login With Amazon access tokens are required to use this sample.
***
This sample uses two different BLLs. One BLL communicates with two potentiometers and sends their readings to the main thread, where they are interpreted as XY coordinates. Lines are drawn between the coordinates to make pictures. A second BLL gets readings from an accelerometer, and when these readings exceed a threshold, the drawing is erased.
***
This sample shows how to integrate the Sharp GP2Y0A02YK0F (available as Sparkfun SEN-08958) long range infrared proximity sensor with Kinoma Create. The analog sensor supports range readings between 15 and 150cm. The app displays the range reading and plays a beep sound that increases in frequency as you get closer to the sensor.
***
This sample uses a BLL to poll values from an analog sensor. It graphs these values using a KPR Canvas object.
***
BLL and sample application for the Honeywell HIH-4030 humidity sensor. Includes a BLL simulator for use in Kinoma Studio and device BLL for use on Kinoma Create. The sample also uses the Texas Instruments TMP102 temperature sensor to provide a temperature compensated humidity reading. The code demonstrates how to chain sensor readings using KPR Messages invoked from the main screen.
***
This sample sends HTTP requests to the Initial State REST API to upload sensor data to a data bucket. The values are read from an analog sensor plugged into Pin 51. Before running the app, sign up for a free Initial State account and replace the dummy text in the code with your Bucket ID and Access Key, shown in your Bucket's settings.
***
This sample sends HTTP requests to the Xively API to upload sensor data to a stream. The values are read from an analog sensor. Before running the app, sign up for a free Xively account and replace the dummy text in the code with your API Key, Feed ID and Sensor ID.
***
This sample shows how to use the MaxBotix LV-MaxSonar-EZ MB1010 Sonar range finder with Kinoma Create. The BLL reads the MB1010 analog voltage pin and converts the voltage measured to range in inches.
***
This sample shows how to use the SparkFun UV Sensor Breakout with Kinoma Create. The ML8511 UV Sensor from LAPIS Semiconductor provides a UV intensity reading through its analog output. The sample application displays the current sensor intensity value and the UV Index derived from it. The UV Index calculation may require calibration for your part of the world.
***
The sample makes your heartbeat visible on the screen of Kinoma Create. Using the Pulse Sensor from pulsesensor.com (available as Sparkfun SEN-11574), the BLL monitors the analog signal to detect beats. The BLL is based on the sample Arduino code from pulsesensor.com, converted to JavaScript and modified for optimal use with KinomaJS.
***
Stripped-down app that prints a value from an analog input pin onto the Kinoma Create's screen. Demonstrates how to implement an analog pin BLL in KinomaJS.
***
This sample shows how to implement a BLL to read from an analog temperature sensor (TMP36 in this case) and display the results to the Kinoma Create's screen.
***
This sample demonstrates how to use an analog trimpot to control the media player volume level. Both device and simulator BLLs are provided. The sample was developed using the Suntan TSR-3386U 10K trimpot available from SparkFun as part number COM-09806. The displayed volume control is implemented using KPR containers and skins.
***
This sample shows how to implement a simple animated sprite. The frames are rendered from a horizontal image strip wrapped by a KinomaJS texture and skin. The skin is bound to a KinomaJS content that drives the animation using an interval timer.
***
This sample provides a collection of KinomaJS behaviors for implementing animations commonly found in user interfaces. Examples show how to apply rotation, clipping, translation, fading and blinking behaviors to KinomaJS containers. Easing functions are supported to further customize the animations. A sequencer behavior leverages JavaScript 6 Promises to drive sequential and parallel animations.
***
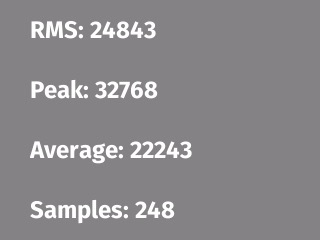
This sample monitors the audio level using the microphone. The audioin BLL records audio samples, which it uses the calculate the peak and average sample levels, as well as the power level (RMS). The results are displayed in realtime by the application, which also adjusts the screen color in real time: black for quiet, white for loud, and grays in-between.
***
Demonstrates how to record and play up to 30 seconds of audio with Kinoma Create’s built-in microphone and speaker.
***
Bouncing ball animation example. Each ball is created as a content using different variants from an image skin. The balls travel by changing the content coordinates over time. This example is written using the KPR ECMAScript programming APIs and demonstrates how to use image skins and content timers.
***
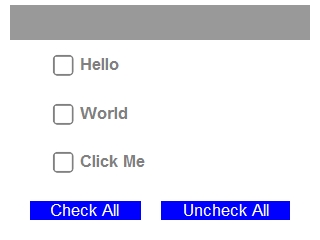
This basic example demonstrates how to use the Checkbox object from the Controls library. In addition to general setup, one option for implementing "Check all" is also shown.
***
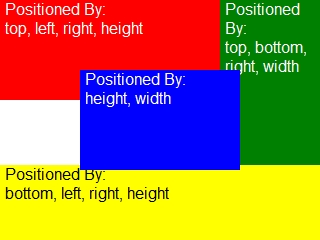
This basic example shows how coordinates are used to specify the position and size of contents relative to their container. The example also uses the JavaScript Array.prototype.map() function to build a container list from an array of instantiating data.
***
This basic example shows how to display a dialog box and handle user input. Due to the size of the on-screen keyboard, this example works best with the "Desktop" and "Nexus One" / "iPhone" simulators.
***
This basic example shows how to distribute events across the container hierarchy to simultaneously update multiple UI elements.
***
This basic example demonstrates how to dynamically build a scrolling list from a simple array of items. Tapping a list item triggers an action. Each list item also includes an embedded button (in blue) that triggers a different action when tapped.
***
This basic example makes a request to a simple web service to generate the MD5 hash of a string. The example demonstrates making requests using JSON, processing JSON responses and basic error handling.
***
This sample demonstrates how to implement a BLE Apple Notification Center Service (ANCS) consumer. After pairing an iPhone with the application, received text, e-mail and phone call notifications are displayed on the Kinoma Create screen. Both BLE central and peripheral roles are supported by this app, which shows how to advertise the ANCS service solicitation and connect with the ANCS provider.
***
Clap into the Kinoma Create microphone to turn on/off a light! This sample controls the BLE Satechi IQ Plug by monitoring the recorded audio level in real time and enabling the plug when the audio level reaches a peak threshold. The IQ Plug is discovered by name and controlled by writing to it's control characteristic.
***
This BLE sample shows how to discover and control the Colorific LED light bulb. An interactive touch color wheel displayed on the Kinoma Create screen is used to change the bulb color in real time. This example additionally shows how to configure the BLE connection intervals to achieve higher responsiveness when controlling BLE peripherals.
***
The Griffin Technology PowerMate BLE control knob is a wireless controller that can be intergrated into other projects. This BLE sample app shows how to discover the button's primary GATT service, connect, detect button presses and left/right spins.
***
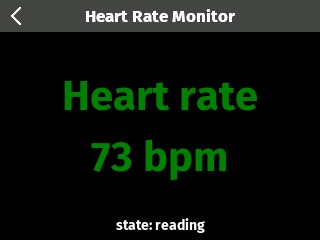
This sample app demonstrates how to build a BLE central application that communicates with a BLE heart rate monitor. Once connected to the monitor, the app discovers both the Bluetooth Heart Rate service (0x180D) and Heart Rate Measurement characteristic (0x2A37). Notifications are requested on the heart rate measurement characteristic, allowing the app to display the beats per minute. This app can also be used as a companion to the ble-heart-rate-peripheral sample app.
***
This sample app demonstrates how to build a BLE peripheral application that simulates a heart rate monitor. As a peripheral the app advertises the Generic Access (0x1800), Device Information (0x180A), Heart Rate (0x180D) and Battery (0x180F) GATT services. Once connected to a BLE client, the app simulates a heart rate monitor by writing measurement values to it's local GATT database, which in turn automatically notifies the connected client. The app can be paired with any mobile app (e.g. Polar Beat) that communicates with BLE heart rate monitors, or as a companion to the ble-heart-rate-monitor sample app.
***
This sample app integrates Kinoma Create with the Miselu C.24 wireless MIDI keyboard. Notes played on the keyboard are displayed in real time on the Kinoma Create screen and audio played through the Kinoma Create speaker. The BLE app interfaces to the keyboard as an Apple Bluetooth MIDI client. This app demonstrates full BLE service and characteristic discovery, enabling notifications, configuring high performance connections and audio synthesis.
***
The Sony MESH Tags are small BLE peripherals dedicated to specific functions. This sample app shows how to discover and receive button press/hold notifications from the MESH Button Tag. The BLE app first establishes a secure and encrypted connection as required by the Tag. Once connected and services/characteristics discovered, the app displays button presses on the Kinoma Create screen.
***
The Satechi IQ Plug lets you control electronic devices and appliances from Bluetooth enabled phones. This BLE sample app shows how to connect to and toggle the plug on/off from the Kinoma Create touch screen. The app discovers the Satechi IQ plug by matching the device name broadcast in BLE scan response packets. Once connected, the app controls the plug by writing commands to the IQ plug's control characteristic.
***
This BLE sample app interfaces with the Blue Maestro Tempo Environment Monitor to display the measured temperature, relative humidity and barometric pressure on the Kinoma Create screen. The Tempo provides these measurements in BLE scan response packets as custom manufacturer advertisement data. The app shows how to parse the advertisement data to extract the sensor measurements.
***
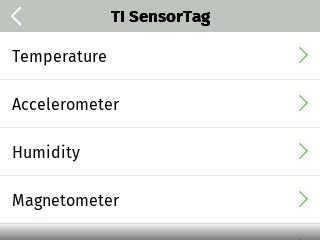
The TI SensorTag is a BLE developer platform for prototyping IoT devices. This sample app shows how to interface with each of the on-board BLE sensor services and displays the sensor data on the Kinoma Create screen.
***
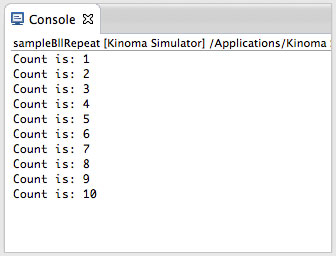
A sample that demonstrates how to repeatedly run a Kinoma Blinking Light Library (BLL). This is useful when, for instance, polling a sensor. The example calls a BLL that traces to the console 10 times and then stops the repetition.
***
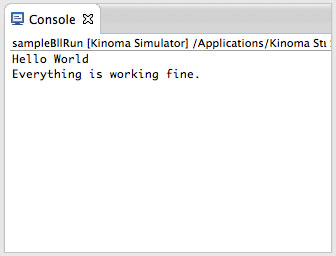
A sample that demonstrates how to run a Kinoma Blinking Light Library (BLL) once. This sample shows how to pass parameters to a BLL, receive them in the BLL, and get results back from a BLL.
***
This example demonstrates how to implement an embedded web view container. The code embeds the web view with a browser container. This example demonstrates how to display a web page in the browser, support browser forward/backwards navigation, implement callbacks when the web page is loading/loaded, display a busy indicator using the MobileFramework and use anchor references to containers. Note that the browser container is not available on Windows or Kinoma Create.
***
A simple camera app supporting live preview and capture. This example demonstrates how to integrate the camera media reader with a picture container, use the Files object to write the captured image to storage, implement screen transitions, detect the platform at runtime, adapt container layouts to device orientation changes, use canvas to implement a button and play one-shot sounds. Note - camera support is currently not supported on Kinoma Create, but this app includes a mockup implementation for the Kinoma Studio desktop simulator.
***
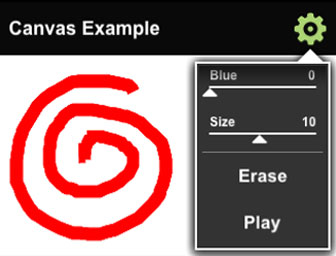
This mobile framework example demonstrates how to use the HTML 2D Canvas API. Tap the settings icon to select the drawing color and line thickness. The main container provides a 2D canvas to draw on. Select the ‘Play’ option from the settings menu to replay your drawing. This example shows how to use the Kinoma ECMAScript API to build and draw on a HTML Canvas 2D Context.
***
Clare is an interactive animation using Canvas, with three modes: scan, pleasant surprise, and track, all accompanied by blinking and saccades of the eyes. The first two modes are randomly triggered, but the last responds to touch. The geometry is primarily composed of quadratic Bézier curves, and the eyes take advantage of the asymmetry available in the radial gradient. Every frame is recomputed using a periodic KPR content timer that triggers an elastic state machine.
***
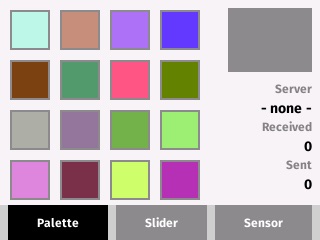
This client app is intended to be run simultaneously with the "coap-server" example and demonstrates how to implement a CoAP protocol client. The app sends an observe request to the Color server running on the same network and receives updates from that server. The client can send a new color by choosing from a palette, slider or RGB color sensor (TCS34725). This example is written using the KinomaJS programming APIs.
***
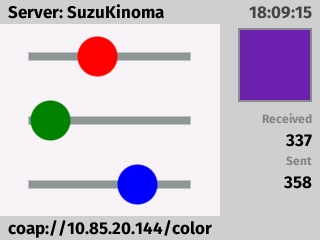
This server app is intended to be run simultaneously with the "coap-client" example and demonstrates how to implement a CoAP protocol server. The app serves color information and the server name to clients. The server app also changes the color of an attached tri-color LED (Sparkfun 10821) to match the server's info. Since CoAP is a standard protocol, you can use other CoAP clients with the server, such as the Ruby CoAP module. See scripts/test.rb for further information. This example is written using the KinomaJS programming APIs.
***
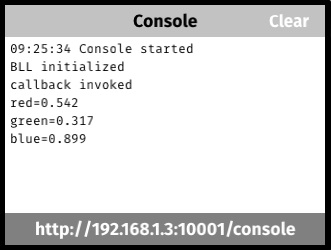
This sample application demonstrates how to display a simple console for logging debugging messages on Kinoma Create. New messages are added to the end of the console log and auto-scrolled into view. The console log can also be viewed in a web browser. Refer to the source code for details.
***
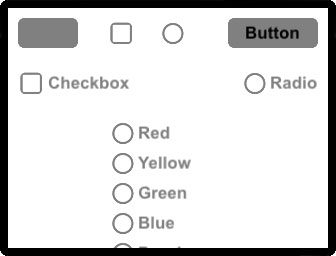
This example demonstrates how to integrate MobileFramework buttons and behaviors into your application. Button types include push, checkbox, radio and radio group.
***
This Kinoma Create application is the remote DIAL client for the dial-remote example application. The application can be launched, quit and configured by the dial-remote app. DIAL client applications can receive launch configuration parameters by supplying a /dial handler. The parameters are delivered is the handler's message query property. The number of balls displayed can be configured by the dial-remote app.
***
This MobileFramework application demonstrates how to use KPR DIAL to remotely launch, configure and quit the dial-client application installed on Kinoma Create. The dial-client application must be installed on Kinoma Create. KPR DIAL uses SSDP to discover DIAL servers and DIAL requests are issued to the remote DIAL server. The target DIAL application name is the KPR application id. DIAL uses a HTTP POST to launch applications. The body of the request contains the parameters passed to the app.
***
This example demonstrates how to setup and display MobileFramework dialogs. Various common controls are integrated into the dialog samples and selected values are output when the dialogs are dismissed. Dialogs are built from a list of items returned by the onDescribe() dialog behavior handler function.
***
Uses a digital pin to read input from a physical button. When pressed, it triggers an event in the application which removes a letter from the string 'Hello World!' on the Kinoma Create's screen. Demonstrates the set up and integration of a digital input pin BLL in KinomaJS.
***
This client app runs with the "digital-light-websockets-server" example. It acts as a companion app that can switch on and off an LED hooked up to the server-side Kinoma Create. This example shows how to discover servers using the built-in SSDP support, create and invoke messages to the server using WebSockets, and how to keep the UI of multiple client apps in sync with the server.
***
This server app runs with the "digital-light-websockets-client" example. This example shows how to connect to one or more clients using the built-in SSDP support and implement a BLL to turn on and off an LED in response to client commands sent via WebSockets. The server keeps all the clients synced with the state of the LED.
***
Uses a digital pin to turn on and off an LED when a button is pressed on screen. Demonstrates the set up and integration of a digital output pin BLL in KinomaJS.
***
This app demonstrates how to use a digital pin to read input from a physical button and use sub-pixel rendering to get smooth animation. It is a simple reflex testing game to play on a Kinoma Create. Three sheep will attempt to run across the screen, and the player's goal is to tap the button before they make it all the way across.
***
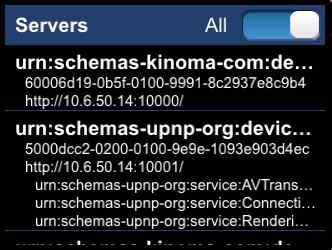
This client app is intended to be run simultaneously with the "device-discovery-server" example and demonstrates how to build a companion app that discovers and interacts with a device. The client discovers all "com.marvell.kinoma.example.discoveryserver" servers on the same network. For each server discovered, the client displays a color swatch in a vertically scrolling container. The color is requested from the server by invoking the server's /color handler. The list is updated on-the-fly as servers are discovered and lost. KPR provides device discovery via built-in SSDP support. This example shows how to discover servers using the built-in SSDP support, create and invoke a cross-application message, and how to dynamically build a scrolling container of items.
***
This server app is intended to be run simultaneously with the "device-discovery-client" example and demonstrates how to implement a discoverable device. The app/device is made discoverable by setting the "shared" application property to true. The "color" handler is called remotely by the client and returns a JSON object containing a CSS color string.
***
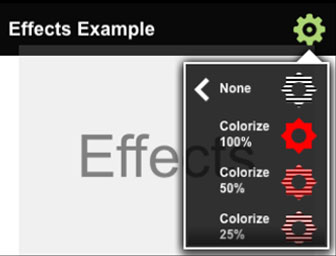
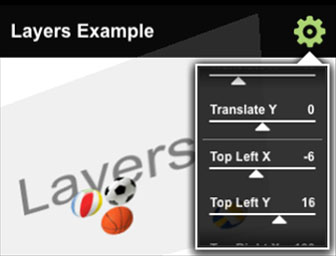
This MobileFramework example demonstrates how to build and apply a variety of effects to KPR layers and pictures. Tap the settings icon to display and select from a scrolling menu of effect types. The effect is applied to the ‘Effect’ layer. Tap the ‘Play’ button at the bottom of the menu to apply the selected effect to a bouncing balls animation. This example shows how to build and apply KPR effects using the Kinoma ECMAScript API.
Changes the brightness of a PWM LED based on the reading from an analog sensor. Demonstrates the use of the built-in analog BLL that works on a variety of sensors including potentiometers and photoresistors. Also demonstrates the use of a user-defined BLL for the LED.
***
Toggles an LED connected to Kinoma Element on and off every second. Demonstrates the set up of a simple digital BLL.
***
Toggles an LED connected to Kinoma Element on and off whenever a button is pressed. Demonstrates the use of the built-in digital BLL for the LED and a user-defined BLL for the button. Also demonstrates the process of setting up two BLLs such that the reading of one is used to write the other.
***
This application for Kinoma Element changes the color of a PWM tri-color LED to the color sensed by a TCS34725 RGB color sensor. Demonstrates the process of setting up two BLLs such that the reading of one is used to write the other.
***
This client app runs with the "element-http-server" example. It sends the message "Hello" and receives a response that says "Hello back!" if the server is active.
***
This server app can be run with the "element-http-client" example or by sending a request by other means. The HTTP server responds with an echo of the body of each request received.
***
Obtains the current temperature from an I2C temperature sensor (TMP102) and traces the value every second. Demonstrates the set up and integration of an I2C BLL on Kinoma Element.
***
Takes a reading from an analog sensor every three seconds and sends data to an Initial State bucket. Data is logged and can be visualized as a graph or saved in a file and analyzed. Demonstrates the set up and integration of an analog BLL and use of the HTTPClient module to send data to a web service.
***
An simple app for Kinoma Element that shows how to turn a continuous rotation servo clockwise and counterclockwise.
***
This simple example controls the position of a hobby servo (on pin 9) using input from an analog controller such as a potentiometer, accelerometer, or sensors for proximity, temperature, moisture, flexion etc. on pin 3. For maximum control and responsiveness, both the sensor and the servo can be calibrated with minimum and maximum values. The example uses built-in BLLs for PWM, analog, power and ground; more complex control sensors may call for a custom BLL. See the KinomaJS Tutorial "Building your Own BLLs" for a walkthrough.
***
Reads the temperature from an I2C temperature sensor (TMP102) and changes the color of an RGB LED accordingly. Demonstrates the set up and integration of I2C and PWM BLLs and the process of setting up two BLLs such that the reading of one is used to write the other.
***
Reads a capactive touch sensor and toggles a Tessel relay module when tapped. Demonstrates how to configure digital input and output sensors using the built-in digital BLL from the Pins module.
***
A sample by Andrew Chalkley. Calls a web service created by the developer and changes the display on an 8x8 LED matrix (Adafruit product ID 1857) to one of three emojis based on the command received. Command can be changed by selecting an emoji on http://wifigotchi.com before running the application. Demonstrates the use of the HTTPClient module and an I2C sensor.
***
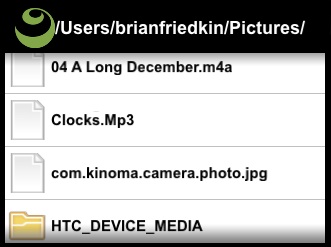
This MobileFramework example demonstrates how to use the global KPR Files object to iterate local files and directories. The application displays the results in a scrolling list view and provides for deep browsing into nested directories. In addition, previews are supported for image, audio and video files. This example is useful for understanding how to use the Files iterator to iterate over a directory, distinguish between file and directory results, command and screen handler behaviors and building scrolling list-based views.
***
This application demonstrates how to use the global KPR Files object. KPR Files provides APIs for reading and writing text, binary, JSON and XML files, and manipulating/iterating directories.
***
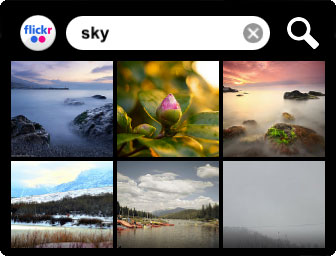
This sample code demonstrates how to implement an interactive scrolling photo thumbnail grid. Tapping the photo thumbnail opens the full size image using a zoom transition. The image thumbnails are retrieved from a Flickr public feed using a tag search. The resulting data set is delivered in JSON format. This is a good example of how to display images, adapt the layout to device orientation changes, use tool buttons or swipe to navigate between photos, invoke a message to fetch data from a REST API and MobileFramework screen open/close transitions.
***
A minimal application that creates a full-screen container and displays the text "Hello, KPR". Tapping the container changes the background color. Useful for understanding how to build a basic KPR application.
***
This application changes the MainContainer's skin to the color sensed by a TCS34725 RGB color sensor. R, G, and B readings are sent from the BLL to the main thread, in which they are converted to hex notation.
***
BLL and sample application for the Hover board touchless gesture sensor from http://hoverlabs.co. Includes a BLL simulator for use in Kinoma Studio and device BLL for use on Kinoma Create. Demonstrates how to write a BLL that uses both I2C and Digital pins, and that changes the direction of Digital pins at runtime.
***
This project builds on top of the i2c-nfc sample by using the same Adafruit PN532 NFC/RFID Controller shield to create an interactive game that makes use of the NFC cards as a "controller". The user places a card on the reader and is able to select an avatar (or “monster”) from about 15 options. The program takes advantage of the fact that data can also be written to a NFC card and uses it as a storage medium: the user’s choice is effectively serialized onto the card as JSON data, and the card can now be brought to another Kinoma Create where the companion project i2c-monster-mayhem-gumball is running to proceed with gameplay.
***
This project is the companion project to i2c-monster-mayhem, and requires a properly programmed NFC card from i2c-monster-mayhem in order to properly work. The user places the preprogrammed card onto the NFC reader and then plays a simple memory game. All the possible candidate “monsters” scroll by, and once the correct avatar is shown (the one initially chosen by the user and programmed onto the card), he/she must quickly remove the card from the reader in order to win the game and receive a gumball. The user is given three tries to do so. If all attempts have been exhausted, then the user must select another monster with a Kinoma Create running i2c-monster-mayhem and reprogram their card.
***
This sample shows how to use the Adafruit PN532 NFC/RFID Controller Shield for Arduino with Kinoma Create. The BLL can discover RFID sensors, as well as read and write the data area on MiFare Classic cards. The BLL communicates over I2C, and can be easily adapted to work with other NFC devices based on the Philips PN532 NFC Controller. The sample applications shows how to display the ID of the discovered RFID.
***
Obtains the current temperature from an I2C temperature sensor and displays it on the Kinoma Create's screen. Demonstrates the set up and integration of an I2C BLL in KinomaJS.
***
This sample shows how to read the Tessel Accelerometer Module which uses the Freescale MMA8452Q 3-Axis Accelerometer. The example displays the values of the sensor in real-time and animates a ball based on the X and Y values of the accelerometer. The application and BLL can be easily adapted to other accelerometers.
***
This sample uses the Tessel Climate Module to retrieve the humidity and temperature values from a Silicon Labs Si7020 sensor. The BLL performs performs necessary calculations to transform the raw sensor data to values convenient for the application to display. The application can easily be adapted for use with other humidity and temperature sensors.
***
This sample shows how to integrate the Sparkfun Touch Shield for Arduino with Kinoma Create. The Touch Shield uses a Freescale MPR121 sensor controller to communicate multi-touch over I2C. The application displays the multi-touch results in realtime on the Kinoma Create screen.
***
This sample integrates the Sparkfun Infrared Proximity Breakout board with Kinoma Create. The Vishay VCNL4000 part integrates a proximity sensor, ambient light sensor, and infrared emitter. The sensor communicates over I2C, and the sample application displays both proximity and the ambient light levels.
***
KinomaJS sample for reading an I2C Wii Nunchuck. This project uses the Solarbotic adapter to interface with the I2C line. Values read include the x-y joystick, c and z buttons, and the in-controller 3-axis accelerometer.
***
This ECMAScript API example displays a synchronized animation built with 256 balls/sprites. Each sprite’s position and size is changed every screen update. A content clock is used to update the display every screen refresh. Tap the screen to change the animation mode. This example shows how to use KPR content clocks, textures/skins, behaviors and content coordinates to achieve full frame rate animations. Also contains icon resources required to allow testing of iOS export from Kinoma Studio.
***
This ECMAScript API example displays a synchronized vortex animation built with text sprites. Each sprite’s position and text size is changed every screen update. A content clock is used to update the display every screen refresh. Tap the screen to change the animation mode. This example shows how to use KPR content clocks, textures/skins, styles, behaviors and content coordinates to achieve full frame rate animations.
***
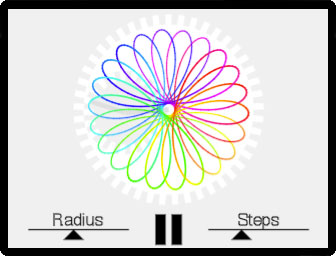
Uses Canvas 2D to implement a virtual hypotrochoid device. Custom sliders control the radius and steps. This application demonstrates how to use canvas containers to render 2D drawing contexts, delegate and notify behaviors using container.distribute, and implement a basic touch slider control.
***
This MobileFramework example demonstrates how to manipulate KPR layers using KinomaJS. Tap the settings icon to display and select from a scrolling menu of layer settings. Use the slider controls to adjust the layer’s origin, scale, skew, translation, opacity and other properties. Tap the ‘Play’ button at the bottom of the menu to display a bouncing ball animation within the layer.
***
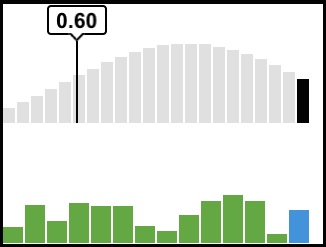
This sample shows how to use the LevelMeterWithProbe object found in the sampleGraph module of the built-in Creations library. You can use the object to graph data over time. Configurable options include the number of samples and colors of the graph bars. This is the same object used by the Pin Explorer application. If you press and hold on the graph it freezes the current samples. When the samples are frozen you can slide your finger over the samples to view their values.
***
This MobileFramework application shows one approach for integrating display of the Apache License NOTICE file into a KinomaJS application. Refer to the Frequently Asked Questions about KinomaJS and Open Source tech note for details. The application demonstrates how to build a scrolling multi-style text view with active links.
***
This MobileFramework application demonstrates how to build a scrolling list view in KPR. An HTTP request is issued to a web service that returns a JSON array of items. The items are loaded and displayed in the list. Tapping a list item opens a detailed item view. The application also demonstrates how to use a KPR layout to adapt the screen layout on device orientation changes.
***
This example demonstrates how to use the Kinoma Create built-in logging support to capture trace output into a log file. Log files can be viewed and/or removed using the built-in Logs app.
***
This MobileFramework application demonstrates how to access the core media library on iOS, Android and Mac OS platforms to display photos and play media files. The application uses a tabbed view to display photo/video thumbnails and songs. Tapping a media item opens a dedicated media viewer screen. KPR messages are used to request the media items. Note that media library support is not currently available for Kinoma Create or Windows.
***
This MobileFramework application shows how to build a media player using the KPR Media object. Media transport controls are provided to start, stop and seek the media. The controls are displayed over the video and automatically hide/show when needed. Tapping the screen displays the controls. The current play time and duration are displayed and updated. This example demonstrates how to integrate KPR media playback, content timers, and implement skin-based buttons and transitions.
***
This example demonstrates how to use a MobileFramework menu button. The menu button displays the currently-selected item in an active label. When tapped, a modal menu of choices is displayed. The newly selected item is returned to the caller using a handler.
***
This example demonstrates how to use features of the MultiTouch Library to create an interactive image viewer suitable for selecting a cropping area from an image. The image may be panned, zoomed, rotated, tossed, with some animated constraints applied. Interactive gestures include tapping, press and hold, drag, toss, and two finger pinching. The sample's comments discuss the framework used, including the TouchStateMachine and TouchBehavior.
***
Kinoma Create application which allows for browsing multiple images by swiping between them. Supports a wide range of single and multitouch interactions by making use of the slidePictureTouchStates module. These include multitouch pinch to scale and pan, dragging and tossing the image, press and hold to zoom about a particular point, and tapping to zoom to view the entire image again.
***
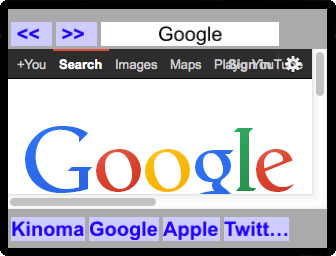
This example demonstrates how to implement OAuth 1.0a (Twitter) and OAuth 2.0 (Google) browser-based login and authentication. The browser is embedded in a web view container. The sample code is useful for understanding how to use a browser container, MobileFramework buttons, handlers to invoke HTTP requests and parse responses and how to implement pure ECMAScript modules with exported methods. Note that the browser container is not available on Windows or Kinoma Create.
***
This example uses a layout container to demonstrate how to adapt layouts to device orientation changes. KPR calls the onMeasureVertically and onMeasureHorizontally methods in layout containers when the device orientation changes. The example dynamically changes the container contents based on the current orientation.
***
Basic digital clock driven by a periodic update implemented by a pair of handlers. The time handler notifies the application of the time change and then invokes the delay handler to wait 1/2 second. Once the delay has completed the time handler is invoked again. The technique is commonly used by applications that require periodic polling of a resource.
***
A minimal application that reads and displays the host platform string read from system.platform. Applications can query the platform string to wrap platform specific code.
***
This application demonstrates how to use a KPR Port object to implement a simple toggle switch. Tap the switch to toggle between the on and off states. The toggle state is displayed as text by another KPR Port object. Various KPR port APIs are covered by this example, including drawImage, drawLabel, fillColor and invalidate.
***
This sample demonstrates how to implement preferences settings that persist across application launches. The selected color swatch is stored across runs. The model.readPreferences function reads stored preferences. The optional third parameter can be used to initialize the preference value the first time. The model.writePreferences function saves the preferences. This example is also useful for learning how to build a container hierarchy using KinomaJS.
***
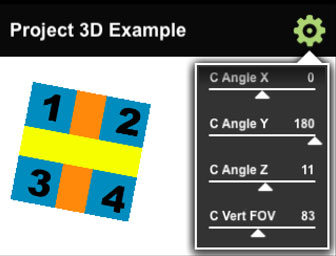
This example demonstrates how to use the projectImage function of the port object. The projectImage function allows a 3D projection to be defined in an intuitive way. Imagine holding a sheet of paper in one hand and a camera in the other. The paper would correspond to a 2D texture, and what the virtual camera sees is projected onto the port. The projectImage function takes 3 parameters: a texture, a billboard description, and a camera description. The billboard description includes the size of the texture, 3D position, and 3D orientation. The camera description is similar to the billboard, but also includes a field of view. Orientations are described as quaternions, which are complex, but the sample includes conversion to and from angles expressed in degrees. The sample presents sliders allowing the various billboard (b) and camera (c) parameters to be exercised.
***
Displays an auto-scrolling horizontal view of photos. Photo images are fetched from a Flickr feed using a proxy handler which returns an array of photo objects. A proxy handler is often used to filter data returned from a web service into a simplified format for use by the host application.
***
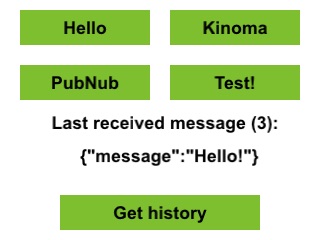
This application sends and receives JSON messages using the PubNub messaging service. It provides a good starting point to learn how to add device-to-device and device-to-web communication to your application. PubNub provides low latency delivery of messages through the cloud. This application includes a full KinomaJS version of PubNub's JavaScript API.
***
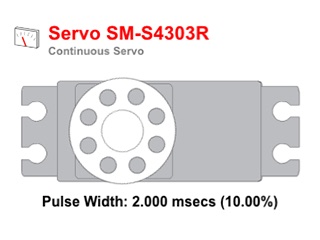
Demonstrates control of 360˚ servos using PWM output from pins on the front (with two-argument pulse-width mode) or back (with one-argument duty-cycle mode). Also demonstrates how to implement a custom parts simulator, and how to use data from an external JSON file.
***
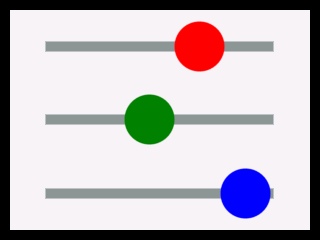
This sample uses red/green/blue sliders to control the color of an RGB LED. The LED is controlled by PWM pins. Each slider is a KPR Canvas object that triggers an onChanged event when you move it to a new position.
***
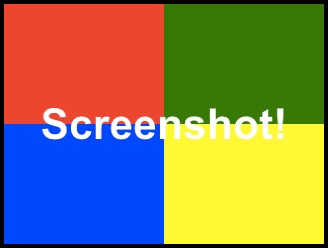
This sample demonstrates how to capture the contents of the KinomaJS application container as a JPEG image file. It then saves that JPEG to disk in the Documents Directory of the target platform.
***
An example that captures from a serial digital camera (VC0706) and displays photographs on the screen when a button (connected to pin 53) is pressed. At startup, the main thread waits for three affirmative Messages back from the camera BLL (one after initialization, one after setting the compression and one after setting the image size). If all goes well, the MainContainer's skin turns green and the user can take a photo by pressing the button.
***
BLL and sample application for the Sparkfun COM-11442 7-Segment serial display. Includes a BLL simulator for use in Kinoma Studio and device BLL for use on Kinoma Create. Demonstrates how to display text strings (ticker tape style) and a digital clock with blinking colon. The device can display all numbers, some letters and special characters. The sample also shows how to integrate the Kinoma Create full screen standard keyboard.
***
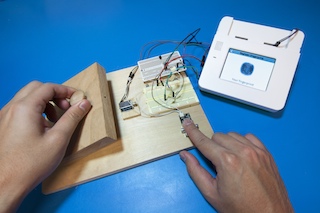
This example integrates a TTL fingerprint scanner (SparkFun GT-511C3) with a 5V solenoid (SparkFun ROB-11015) to prototype a fingerprint locking system. The prototype registers and stores authorized fingerprints on the scanner. Authorized fingerprints can then unlock the door controlled by the solenoid. The prototype was demonstrated at Maker Faire Bay Area 2015 and shows how to control the fingerprint scanner via a serial BLL and the solenoid using a digital output. The prototype also shows how to integrate the Kinoma Create full screen keyboard, play sounds, build scrolling lists and display rotated graphics.
***
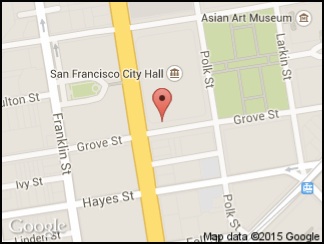
BLL and sample application for the Adafruit Ultimate GPS Breakout, MTK3339 GPS chipset. The app polls the GPS position periodically and displays the position on a map requested from the Google Static Maps API. The map is updated when the position changes.
***
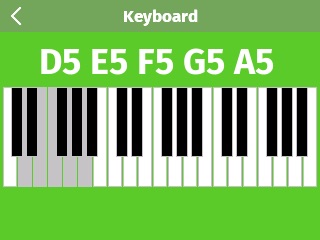
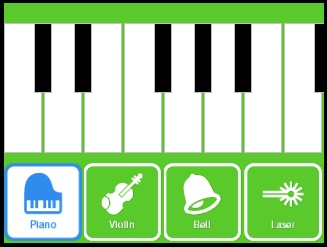
Simple Synth shows you how to synthesize audio in real time for low latency playback on Kinoma Create. Use the on-screen multi-touch keyboard to play up to five simultaneous notes on the sine wave based synthesizer. Additional synthesizer modes have been added in, as well as an optional analog input for volume control.
***
Sketchat, a contraction of "sketch" and "chat", is a "shared whiteboard" application; when something is drawn on one Sketchat, it appears on all others. The application demonstrates how to discover other Sketchats on the network and how they can easily exchange information. The pen color can be chosen using a TCS34725 color sensor. An accelerometer is used so that shaking a Create will clear the canvas. When the application is stopped, its drawing dissapears from other Sketchats.
***
Displays a slideshow of images animating picture scaling, panning and opacity settings to implement Ken Burns style transitions. This example demonstrates how to dynamically add picture containers into the container hierarchy, distribute events to container behaviors, use a content timer to drive animations, display a busy indicator and invoke a HTTP request to fetch a photo collection from a public Flickr feed.
***
This MobileFramework Kinoma Create example streams live radio from the SomaFM service. Channels are selected using a touch controlled scrolling tuner. A music artist image collage is displayed and updated on track changes. This example demonstrates how to use KPR media to play HTTP streams, build custom UI elements with HTML Canvas, use a proxy handler to fetch data from a web service, and use KPR effects and layers to implement an animated image collage. The SomaFM player also supports KPR DIAL and can be controlled remotely by the somafm-remote phone application.
***
This MobileFramework phone application streams live radio from the SomaFM service and can be used to remotely control the somafm-player application. Using KPR DIAL, this example discovers the SomaFM player application running on Kinoma Create and can change channels and the volume level remotely. Channels are selected using a touch-controlled scrolling tuner. A music artist image collage is displayed and updated on track changes. This example demonstrates how to use KPR media to play HTTP streams, build custom UI elements with HTML Canvas, use a proxy handler to fetch data from a web service, and use KPR effects and layers to implement an animated image collage.
***
Displays a mockup camera preview with shutter button. Tapping the button plays a shutter sound. The application calls sound.play to play a WAVE file. This application also demonstrates how to use a transition to simulate the shutter closing and opening.
***
Displays a spinning busy indicator by rotating a custom graphic using a periodic timer. The indicator is displayed half size by setting the graphic's picture scale and origin properties.
***
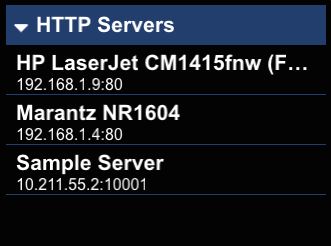
A simple application that shows SSDP usage. The application starts an HTTP server on port 1234, registers a service named "KPR Server". It also looks for available HTTP servers on the local network.
***
This example demonstrates how to use content states to change a button's background and text colors when tapped. The text color is defined by the text style states. The button background color is defined by the skin states.
***
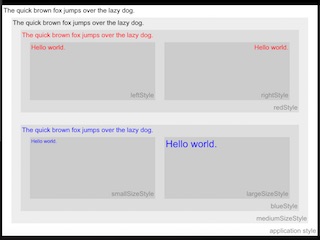
This example demonstrates how KPR cascades styles in the container hierarchy. A content inherits the characteristics of its container style when the characteristics are undefined in the content style. In this example, the applicationStyle defines a style for the root of the container hierarchy and nested containers build on the applicationStyle by overriding various style characteristics, including point size, alignment and color. Note: This example is best viewed on a tablet-sized screen or simulator.
***
This example displays a vertical scrolling column of text formatted with a wide variety of styles. Usage of all the common text style attributes are demonstrated, including font, text style, point size, alignment, leading, color and margins.
***
This MobileFramework example demonstrates how to build a tabbed UI screen. Each tab opens a different style pane. The tabs are placed in the screen footer area and built using the MobileFramework screen's TabFooter object and skinned using the default sample theme tab skins. The tab-to-tab transition is managed by the MobileFramework TabListSwapTransition. You can customize the tab look and behaviors by replacing and/or overriding these objects. For example, you can use the MobileFramework screen's TabLine object to implement a tab bar that can be placed anywhere on the screen and without icons.
***
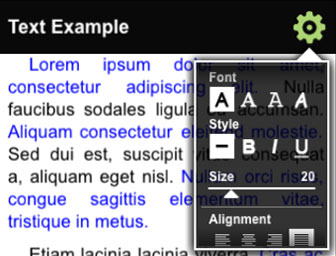
This MobileFramework example demonstrates how to use KinomaJS to get and set various KPR Text and Style properties, including font, point size, style, alignment, indentation and margins. The example also shows how to implement tappable text links and use text spans to display multi-styled text blocks. Tap the settings button to choose from a scrolling menu of text and style options.
***
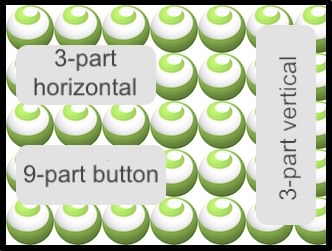
This example demonstrates how to use tiled skins to fill content. Examples of nine part and three part horizontal/vertical tiled skins are provided. The nine part container is a button that changes color (state) when tapped. Additionally this example shows how to use a layer to display rotated text.
***
This example demonstrates how to use different timer techniques: One-shot, interval, repeating, handler.wait and container.wait. An interval timer is used to animate skin states.
***
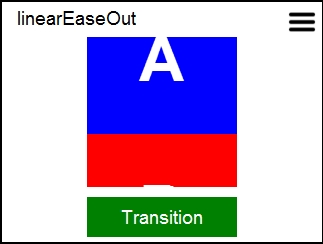
This example demonstrates the array of easing functions available for use when designing transitions. A simple "slide-off" transition is displayed using the selected easing funciton.
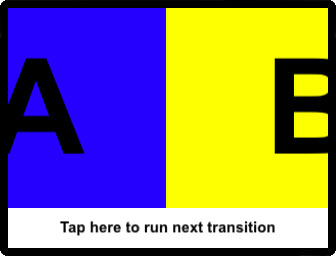
***
This example demonstrates how to use the Transitions library to configure and use a variety of transitions. The host application can further customize each transition by overriding the duration, easing function used for pacing time and specifying whether or not the former content should be removed once the transition completes.
***
This example shows how to configure and capture recorded audio into a WAVE file.
***
This sample application demonstrates how to build a simple web server with KPR. Setting the application 'shared' property to 'true' shares the application as a service on the local network and enables the HTTP server. The sample shows how to support GET and POST requests and how to serve static and dynamic web pages with images. Transactions are displayed in a scrolling log view.
***
This MobileFramework application demonstrates how to implement a WebSocket client in KPR. Coupled with the websocket-server example, this application implements a WebSocket-based chat client. The client discovers and connects to the server using SSDP and exchanges text messages with the server. This application is useful for understanding how to integrate WebSockets, use SSDP to discover server devices, build UIs with editable text fields and transitions.
***
This application demonstrates how to implement a WebSockets server in KPR. Coupled with the websocket-client example, this application implements a WebSocket based chat server. The client discovers and connects to the server using SSDP. Once the connection is established, the client exchanges text messages with the server. This application is useful for understanding how to build a WebSockets server and use KPR Text and Scroller objects to display a scrolling list of messages.
***
This example demonstrates how to issue an HTTP request to the OpenWeatherMap service and use the KPR DOM parsing APIs to parse the XML response. The temperature for the requested city is displayed. This example shows how to invoke a HTTP request to a web service, parse the XML response, display a busy indicator while waiting for the result and how to implement a tappable link which opens in the device browser. Note that browser support may not be available on all platforms.
***
A simple application that shows Zeroconf usage. The application starts a HTTP server on port 1234, registers it with the name service named "KPR Server". It also looks for available HTTP servers on the local network. To run this application in the simulators on Windows, first install Apple iTunes.
***
This example integrates Digi's XBee radio (available as SparkFun WRL-10414) with GE Link light bulbs to build a ZigBee Home Automation gateway with Kinoma Create. The application shows how to commission, discover and control the bulbs on the ZigBee network.
***These examples released under the Apache Foundation license.